ANKLE INSTABILITY
Ankle instability is a condition in which the patient feels as if the ankle is giving way when performing activities of daily living. It usually results from repeated ankle sprains. It can or not be painful and occurs when walking or standing on an uneven surface.
Repetitive injury of the ankle ligaments is the most common cause of ankle instability. Inadequate healing of the sprained ligament or incomplete rehabilitation of the affected ligament can also result in ankle instability. Recurrent injury of the ligaments weakens them even more, aggravating the instability which predisposes to the development of additional ankle problems, like ankle cartilage injuries.
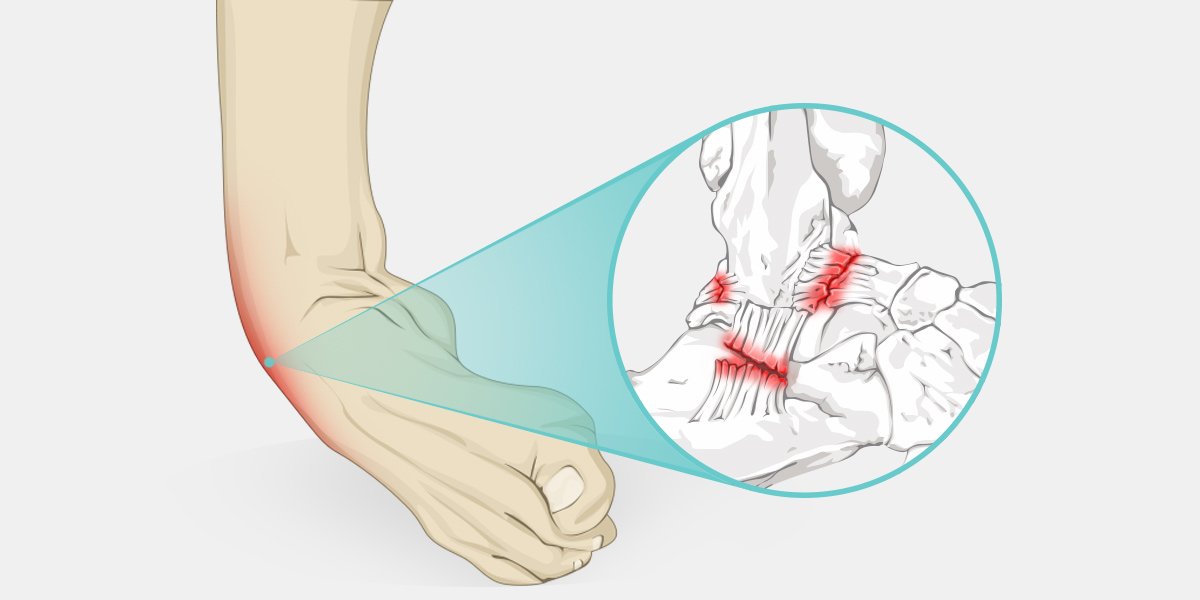
Symptoms include:
-
Pain at the front and on the side of the ankle joint
-
Swelling and tenderness on the outside aspect of the ankle.
-
Persistent discomfort and instability.
-
The unstable ankle may twist inwards repeatedly while walking on uneven surfaces or during a sporting activity.
To diagnose this condition, a complete medical history, including a history of any previous ankle injuries, and a physical examination are essential. An X-ray, CT scan and/or MRI would be required to obtain more information about the injury.
The management of ankle instability depends on the findings of the physical examination and the images. Conservative treatment of the recurrent ankle instability includes physiotherapy to work on strength, balance and range of motion of the joint; bracing to support the affected ankle and prevent further sprains; and analgesics and ice to reduce the pain and inflammation.
Surgery is recommended in patients with a high degree of instability and in those who have failed to respond to non-surgical treatments. Commonly used surgical procedures involve repair or reconstruction of the damaged ligaments along with an assessment of the joint with an ankle arthroscopy.