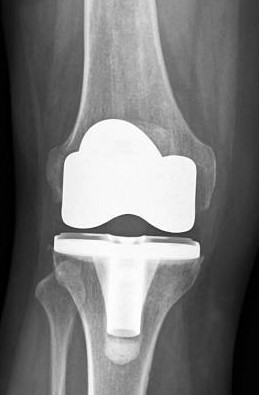
What is a knee replacement?
Knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to resurface a knee damaged by arthritis. Metal and plastic parts are used to cover the ends of the bones that form the knee joint, along with the kneecap.
Various types of arthritis may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis, is the normal degeneration of the joint that affects mostly middle-aged and older adults. This is due to the breakdown of joint cartilage and adjacent bone in the knee. Rheumatoid arthritis, which causes inflammation of the synovial membrane, resulting in excessive synovial fluid and leading to pain and stiffness. Traumatic arthritis, is due to a previous injury, may cause damage to the cartilage of the knee.