HIP ARTHROSCOPY
Arthroscopy is commonly known as keyhole surgery. Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an arthroscope, a small tube with a light and video camera at the end, is inserted into the hip joint. The procedure is performed through very small incisions to diagnose and treat various hip conditions including:
-
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)
-
Removal of torn cartilage or bone chips that cause hip pain
-
Repair a torn labrum, a fibrous cartilage ring on the edge of the hip socket
-
Treating Snapping hip syndrome
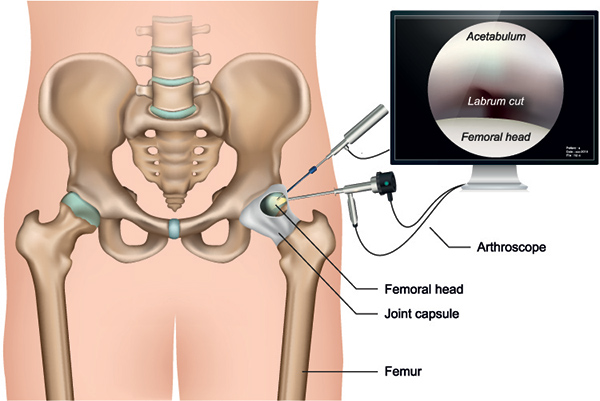
The surgery consists of making 2 or 3 small incisions about 2 cm in length around the hip joint. Through one of the incisions, the arthroscope is inserted. A sterile solution is pumped into the joint to expand it and enlarge the working space. Surgical instruments will be inserted through other tiny incisions to treat the problem. After the surgery, the incisions are closed and covered with a bandage.
Since the hip joint is a large joint with powerful muscles holding it, gentle traction must be applied to create enough space for the instrumentation to fit in.
The advantages of hip arthroscopy over the traditional open hip surgery include:
-
Smaller incisions
-
Minimal trauma to surrounding tissues
-
Less pain
-
Faster recovery
-
Lower infection rate
-
Less scarring
-
Earlier mobilisation
-
Shorter hospital stay